Have you ever wondered what it takes for it to rain? Let’s dive into the science behind rain clouds!
How does it rain?
Rain occurs when water vapor in the air cools and condenses. The droplets form around microscopic particles called cloud condensation nuclei. These water droplets bump each other and condense. Eventually, they get too big and fall, hitting even more water on the way down to earth.
Clouds
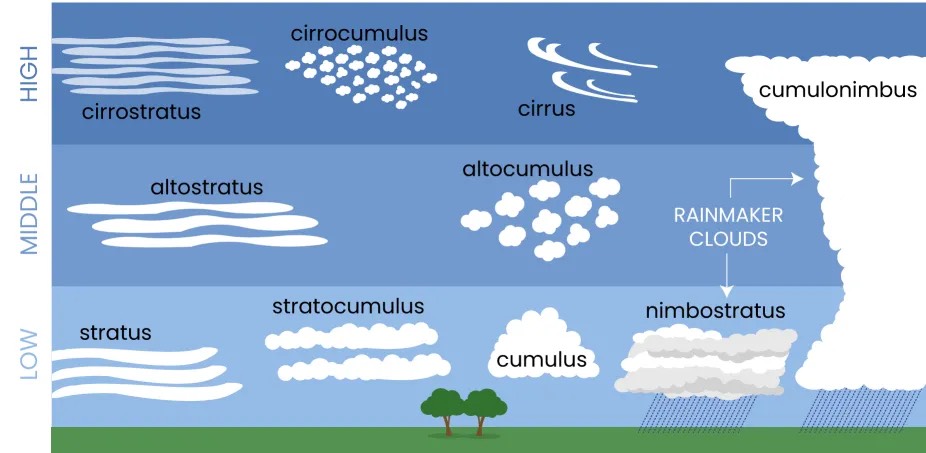
There are 3 primary cloud types: cirrus, cumulus and, and stratus. Cirrus clouds are wispy white clouds in patches or bands. Cumulus clouds are the classic white fluffy, Cotton candy shaped clouds. Stratus clouds are a gray, translucent cloud layer. Cumulus clouds typically bring rain with them. They’re created by strong updrafts of warm, moist air.
How do we predict the weather?
Weather forecasts are made by collecting data about the current state of the atmosphere and using knowledge about how the atmosphere works to make predictions about how it will change. To make these predictions, meteorologists need to understand what’s producing the current weather conditions. They do this by examining a large quantity of data from surface observations, satellite images, radar data, and many more sources.
Cloud seeding
Cloud seeding is a weather modification technique used to improve clouds’ ability to produce precipitation. It works by tiny freezing substrate or dust particles into a cloud to act as condensation nuclei. However, cloud seeding can’t make a cloud. If there are no clouds, or clouds are too small to produce precipitation, then cloud seeding will do nothing. This is why you can’t use cloud seeding to make it rain in a desert.